Diamond Buying Guide
To simplify the diamond buying process we have made the guide to detail out how our filter works for the selection of diamonds.
Please refer below to follow the steps to find the perfect diamond for your jewellery.
1. Shape
Shape is the most crucial point in starting the. selection of diamonds. Select your preferred shape to narrow down your search and compare diamonds. Round is the most common and popular diamond shape. We have a wide range of shapes to choose from. Other unique shapes are cushion, half moon, oval and many more. We have divided the diamonds on the basis of shape into four categories:
- Round diamonds
- Fancy shape diamonds
- Fancy color diamonds
- Diamond pairs

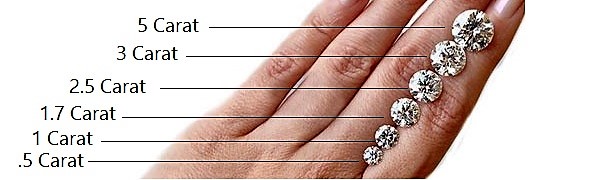
2. Size
Janam has the widest selection when it comes to size options.
Since we have been working with a lot of jewellery brands we understand the requirement of the jewellery industry. And hence we have created the range of diamonds keeping in mind the wide range of requirements all across the globe.
To make the measurements transparent and universal we have put in three parameters to understand the size of each minute diamond.
- Sieve Size
- Diameter of each stone in MM
- Weight of each diamond
The first is the sieve size which is universal. We have even mentioned the diameter of each stone to match with the sieve size and each sieve size and diameter of the diamond has all the weight per stone mentioned to make it moreclear to the users.
After making the final choice of the size you can select the carat weight. The price of the parcel depends on the carat weight of the parcel.
3. Clarity
Diamond clarity refers to absence of any inclusions or blemishes. Due to natural formation of diamonds under high pressure there can be some inclusions.
We follow GIA system of clarity grading:
The GIA Diamond Clarity Scale has 6 categories, some of which are divided, for a total of 11 specific grades.
-
 Flawless (FL) No inclusions and no blemishes visible under 10x magnification
Flawless (FL) No inclusions and no blemishes visible under 10x magnification
Internally Flawless (IF) No inclusions visible under 10x magnification -
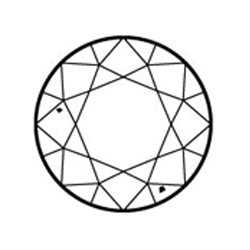 Very, Very Slightly Included (VVS1 and VVS2) Inclusions so slight they are difficult for a skilled grader to see under 10x magnification
Very, Very Slightly Included (VVS1 and VVS2) Inclusions so slight they are difficult for a skilled grader to see under 10x magnification -
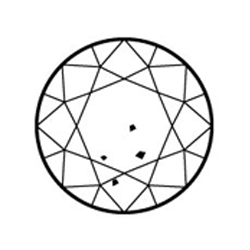 Very Slightly Included (VS1 and VS2) Inclusions are observed with effort under 10x magnification, but can be characterized as minor
Very Slightly Included (VS1 and VS2) Inclusions are observed with effort under 10x magnification, but can be characterized as minor -
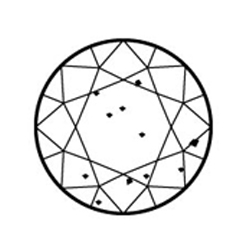 Slightly Included (SI1 and SI2) Inclusions are noticeable under 10x magnification
Slightly Included (SI1 and SI2) Inclusions are noticeable under 10x magnification -
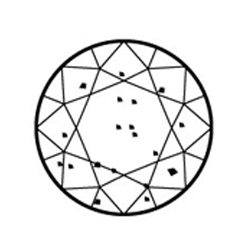 Included (I1, I2, and I3) Inclusions are obvious under 10x magnification which may affect transparency and brilliance
Included (I1, I2, and I3) Inclusions are obvious under 10x magnification which may affect transparency and brilliance
4. Cut
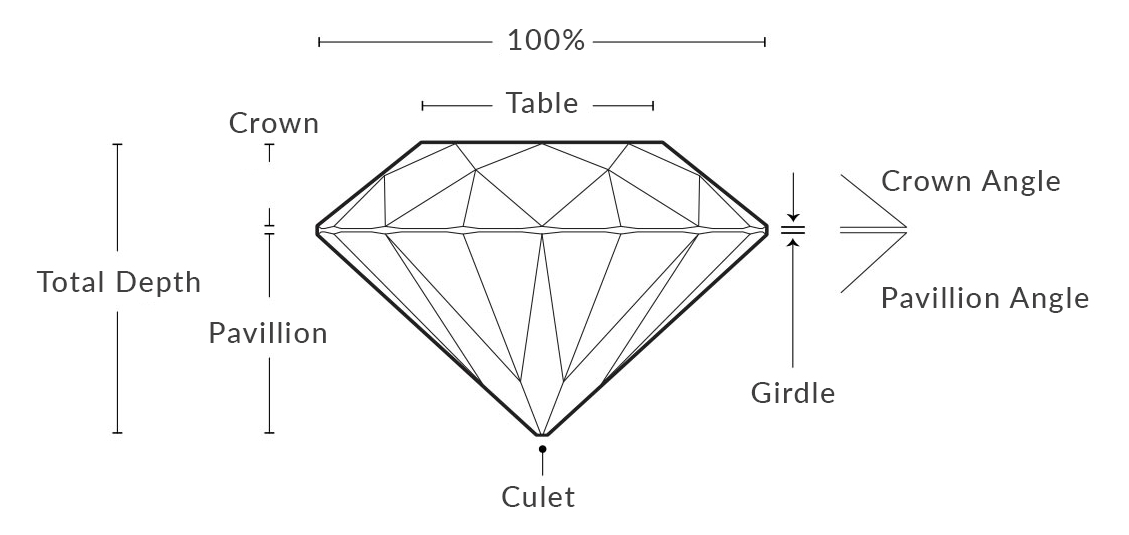
Diamonds are renowned for their ability to transmit light and sparkle so intensely. We often think of a diamond’s cut as shape (round, heart, oval, marquise, pear), but a diamond’s cut grade is really about how well a diamond’s facets interact with light.
Precise artistry and workmanship are required to fashion a stone so its proportions, symmetry and polish deliver the magnificent return of light only possible in a diamond.
-
 EXCELLENT
EXCELLENTThe diamond, which has an even pattern of bright and dark areas, scores in the top category for all grade-setting determinants.
-
 VERY GOOD
VERY GOODThis diamond's grade is determined by brightness, scintillation, and polish. Although no individual proportions would necessarily cause its brightness or scintillation to perform poorly, the combination of this particular set of proportions leads to increased darkness in the pavilion mains.
-
 GOOD
GOODThis diamond's grade is limited by its scintillation. In this case, the somewhat shallow pavilion angle produces dark pavilion mains.
-
 FAIR
FAIRThis diamond's grade is limited by its scintillation. The combination of a shallow crown angle and a somewhat shallow pavilion angle leads to a face-up appearance with a lack of contrast and general darkness.
-
 POOR
POORThis diamond's grade is limited by its weight ratio. Although most of the proportions for this diamond are fairly standard, the extremely thick girdle greatly increases the total depth. Therefore, this diamond's diameter is much smaller than its carat weight would indicate.
5. Color
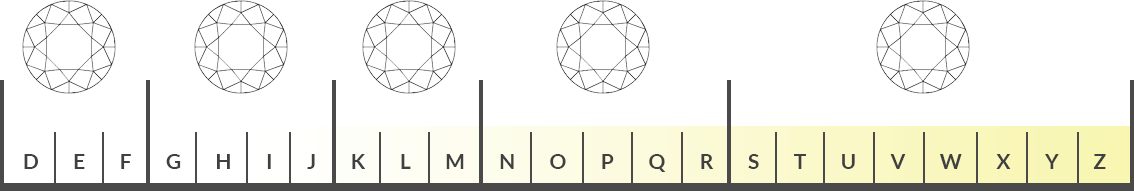
A diamond is graded from (D-Z) on a grading scale. Colorless diamonds are graded from D TO Z. D is colorless and Z is Yellow tint. The more colorless diamond is more value than Z color diamond.
The diamond color evaluation of most gem-quality diamonds is based on the absence of color. A chemically pure and structurally perfect diamond has no hue, like a drop of pure water, and consequently, a higher value. GIA’s D-to-Z diamond color-grading system measures the degree of colorlessness by comparing a stone under controlled lighting and precise viewing conditions to masterstones of established color value.
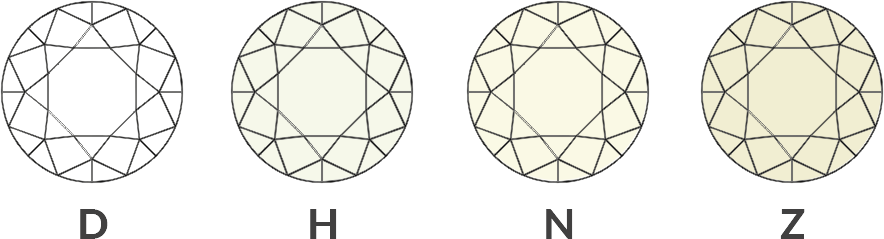
Many of these color distinctions are so subtle that they are invisible to the untrained eye; however, these distinctions make a very big difference in diamond quality and price.
6. Certificate
You can get your diamond parcel verified by Labs such as IGI, GIA and HRD by paying the test fee and getting a certificate. The certification process takes time and depends on which lab you want certification from.